People all over the world are bombarding you with facts and figures. If you want to know which facts are true and false, then you must know the difference between Objective and subjective claims. Also, objective vs. subjective is important to understand the grammatical errors that we often commit.
Before moving ahead, check out some of our latest posts:
How to Choose Good Informative Speech Topics
What is Natural Law Theory in Philosophy?
In today’s world, where we heard heated disagreements, we need the ability to distinguish facts from opinions. An effective argument includes both factual observations and judgments based on those facts. Thus it is essential to understand objective vs. subjective.
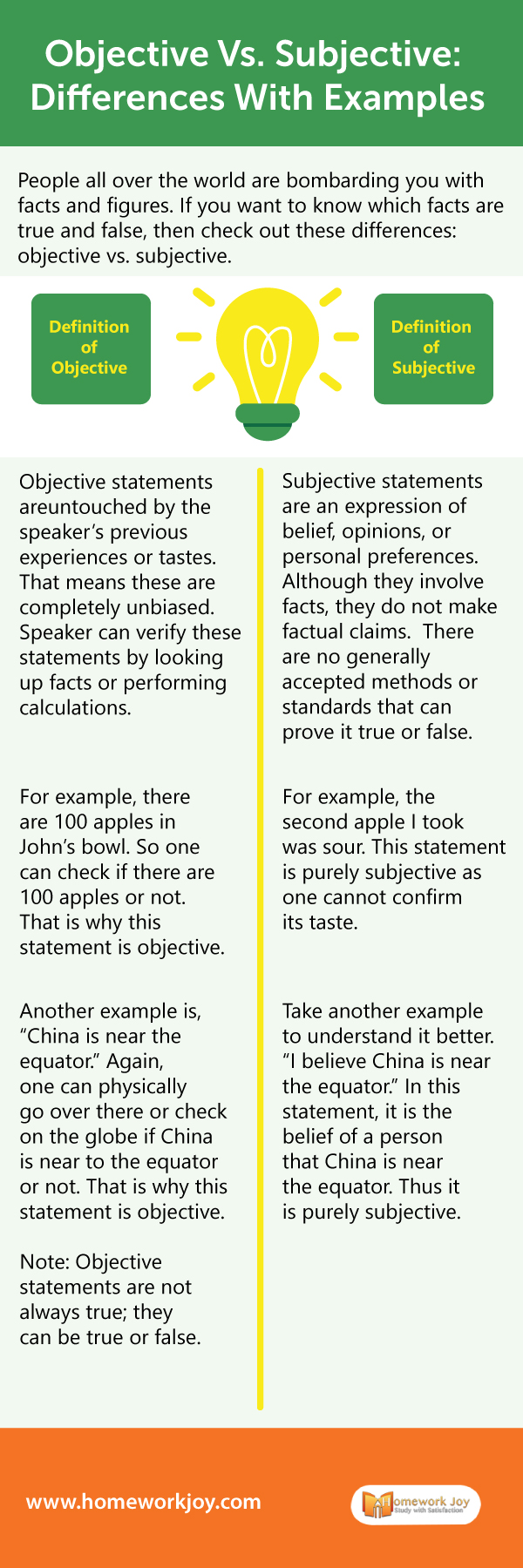
Definition of Objective
Objective statements are untouched by the speaker’s previous experiences or tastes. That means these are completely unbiased.
Speaker can verify these statements by looking up facts or performing calculations.
For example, there are 100 apples in John’s bowl.
So one can check if there are 100 apples or not. That is why this statement is objective.
Another example is, “China is near the equator.” Again, one can physically go over there or check on the globe if China is near to equator or not. That is why this statement is objective.
Note: Objective statements are not always true; they can be true or false.
When to Use Objective?
The objective is an adjective that is not influenced by personal feelings or bias. That is why it is the synonym of impartial or neutral. In grammar, objective refers to nouns or pronouns used as the object in a sentence.
Here are some of its examples:
- He strived to engage in objective reporting, as he is a journalist.
- Before we proceed, we need an objective assessment of the case’s facts.
Definition of Subjective
Subjective statements are an expression of belief, opinions, or personal preferences. Although they involve facts, they do not make factual claims.
There are no generally accepted methods or standards that can prove it true or false.
For example, the second apple I took was sour. This statement is purely subjective as one cannot confirm its taste.
Take another example to understand it better. “I believe China is near the equator.” In this statement, it is the belief of a person that China is near the equator. Thus it is purely subjective.
When to Use Subjective?
On the other hand, subjective means based on individual opinion or experience. In grammar, subjective refers to nouns or pronouns used as the subject of the sentence.
Here are some of its examples:
- My subjective stance is that “The pasta wasn’t very delicious to me.”
- A good journalist doesn’t allow subjective views to contaminate hard news.
So these were some essential differences of objective vs. subjective. If you need more English assignment help, contact our experts now.